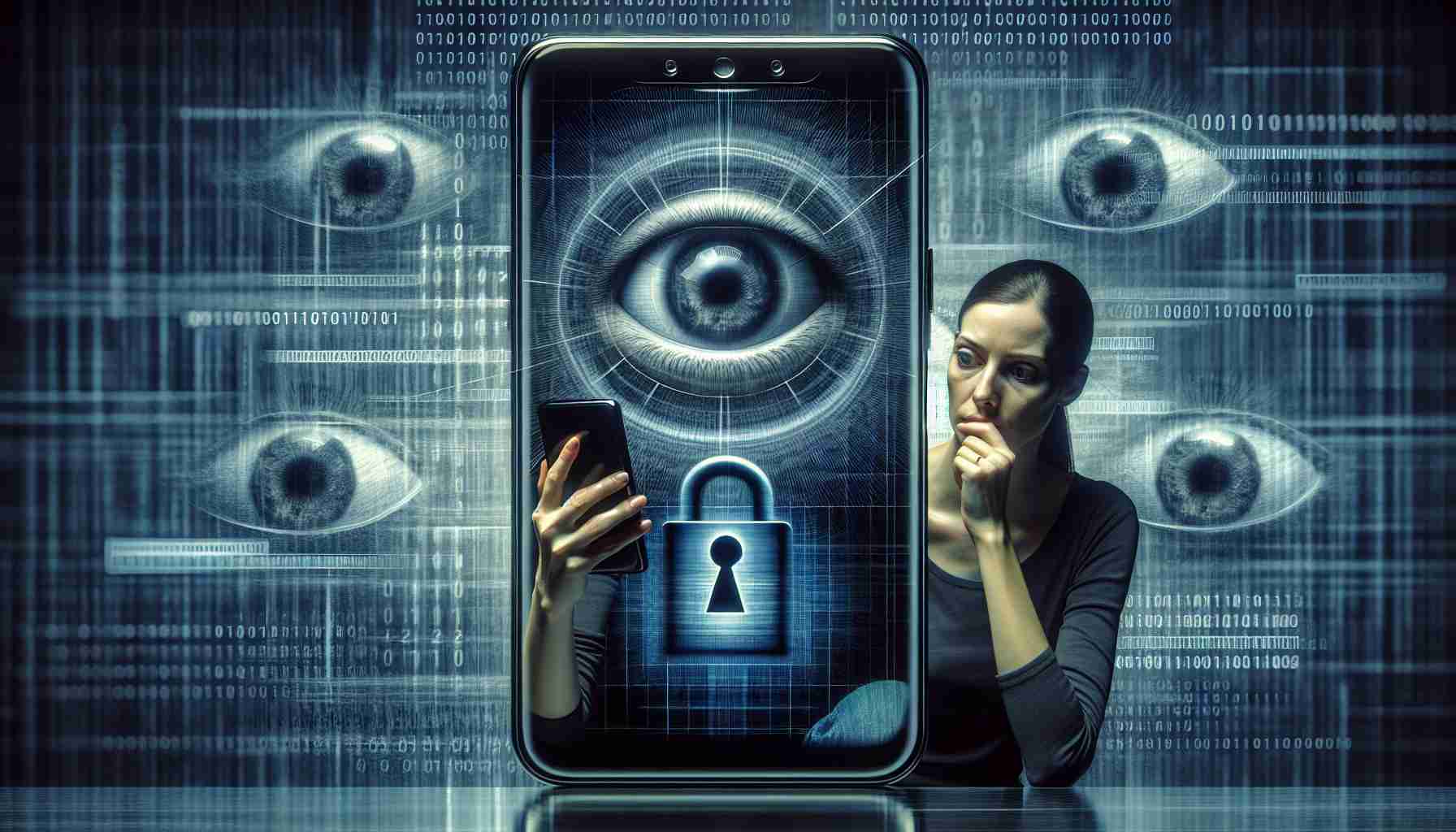
In today’s digital age, the intersection of technology and personal privacy remains a contentious topic. Many users have noticed a striking alignment between their conversations and the advertisements appearing on social media platforms, sparking fears of surveillance through their devices. While technology firms have historically dismissed these notions as unfounded, recent revelations indicate a more complex reality.
CMG Local Solutions, a marketing firm from Atlanta, has gained attention for its innovative approaches to advertising. In 2022, the company achieved remarkable revenue of £22.1 billion, boasting a client list that includes major players like Google, Amazon, and Facebook. Their marketing strategies encompass multiple channels, including search optimisation and email outreach, but one of their offerings stands out: a discreetly managed tool known as “Active Listening.”
This software, shrouded in secrecy, has been linked to the ability to curate advertisements based on ambient conversations. Leaked documents have brought to light details indicating that companies may employ technology to tap into discussions occurring near smart devices such as TVs and speakers. This raises pressing questions: Are consumers truly being monitored continuously, or is this merely an exaggerated fear?
https://youtube.com/watch?v=GKCz4sDENQg
As technology evolves, so too do the concerns surrounding user privacy. The implications of these revelations urge users to be more vigilant about their digital interactions and the extent of data collection that may occur in their daily lives.
Privacy Concerns: The Reality Behind Smartphone Surveillance
In an era where smartphones have become an integral part of daily life, the concerns surrounding privacy and surveillance are more pressing than ever. The mere presence of our devices raises the question: how secure is our personal information? While many users remain blissfully unaware of potential threats, emerging evidence suggests a complex web of data collection practices that extend far beyond typical app behaviour.
What constitutes smartphone surveillance? Surveillance can be any method through which user data is collected, monitored, or analysed without explicit consent. This can include location tracking, microphone access, and various app permissions that often go unchecked by users.
Key questions about smartphone surveillance include:
1. How is user data collected?
Many apps require permissions that allow them to access various device functions, including GPS, camera, and microphone. Users often grant these permissions without fully understanding the implications.
2. What types of data are being collected?
Data can range from geographical locations and call logs to browsing habits and even biometric information. This collection poses risks of intimate details being exposed if the data falls into the wrong hands.
3. Who are the main players?
Apart from well-known technology giants, numerous third-party data brokers acquire user data to sell to marketers and advertisers, blurring the lines of privacy even further.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Smartphone Surveillance
Advantages:
– Personalised Experience: Users often benefit from personalised content and advertising tailored to their preferences, leading to potentially more relevant app interactions.
– Enhanced Services: Location-based services can provide valuable information, such as traffic updates and local deals, which rely on real-time data.
Disadvantages:
– Loss of Privacy: Continuous data collection can lead to significant invasions of privacy, with risks of personal data breaches becoming increasingly common.
– Manipulation Risks: There is a potential for misinformation and manipulation as companies may use collected data to influence consumer behaviour in unethical ways.
Key Challenges and Controversies
One major controversy is the ethical implications of data collection. Many users are unaware of the extent to which their data is monitored and sold, leading to calls for more robust privacy regulations. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe has set a precedent for data protection laws worldwide, yet enforcement and compliance remain challenging.
Moreover, users frequently face a dilemma: use innovations that enhance daily life, or protect their privacy at the cost of convenience. Recent studies indicate that as many as 60% of users do not read app permissions before granting access, highlighting a pressing need for better user education around privacy settings.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the balance between convenience and privacy will remain a focal point for users worldwide. Awareness and proactive measures, like reviewing app permissions and understanding data rights, can empower users in reclaiming control over their personal information. For further information on smartphone privacy standards and user rights, visit Privacy Rights Clearinghouse. The conversation around privacy will undoubtedly evolve, but it’s crucial that individual users engage with the realities of smartphone surveillance for a safer digital experience.