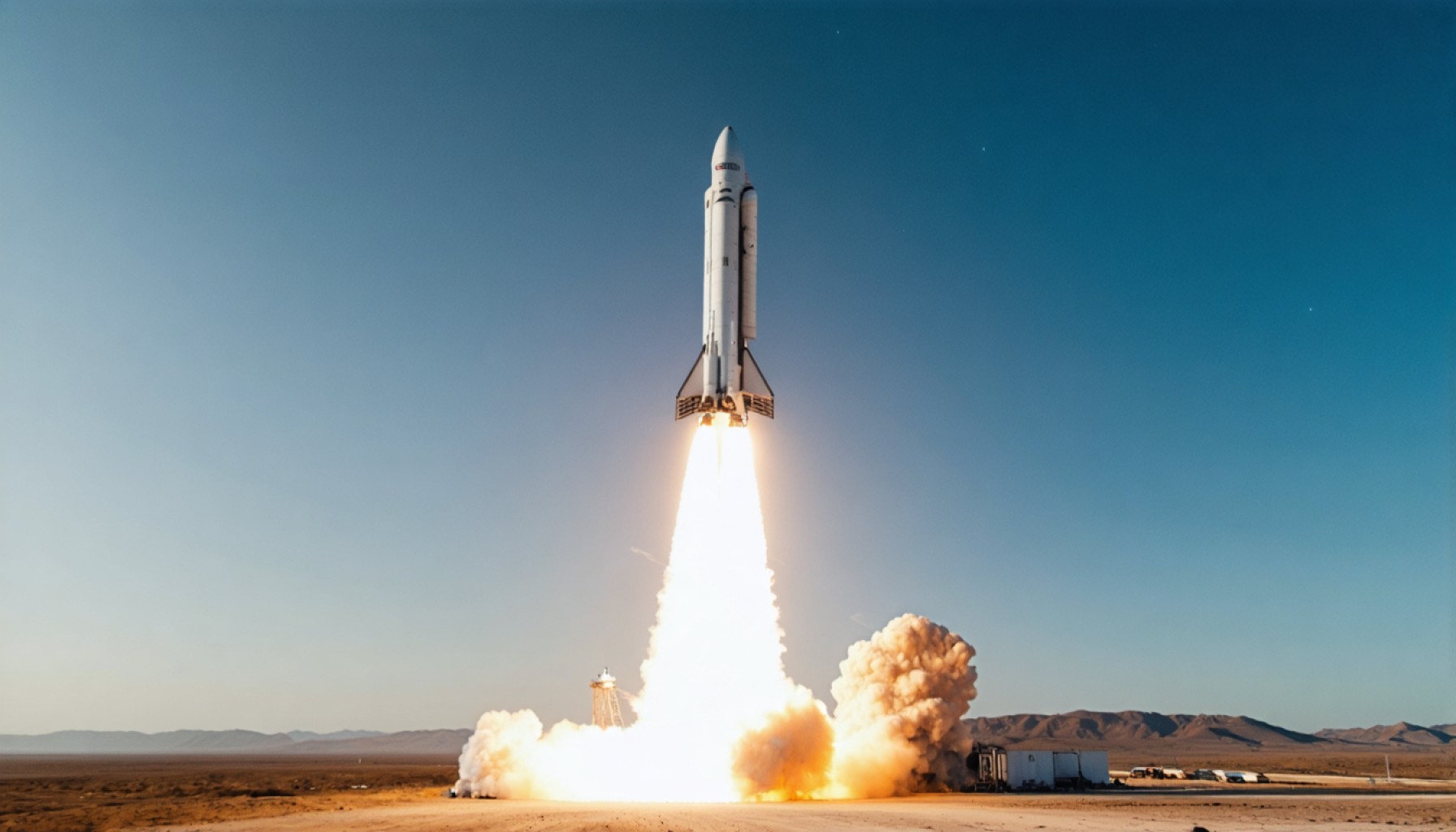
- SpaceX’s Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas, prepares for a pivotal Starship orbital test as part of Elon Musk’s vision for Mars exploration.
- The 403-foot-tall Starship is central to advancing human space travel, with enhanced reliability following a previous failure over the Caribbean.
- The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires a thorough investigation into January’s mishap but tentatively approves the next launch amid scrutiny over SpaceX’s influence.
- Controversial claims suggest Elon Musk’s power may extend to regulatory bodies, sparking debates on corporate influence versus public safety.
- NASA closely monitors the situation, as Starship is crucial for the Artemis program’s lunar ambitions, exemplifying private-public dependence in space exploration.
- The upcoming mission aims to catch the booster mid-air and simulate satellite deployment, pushing engineering boundaries while balancing innovation and responsibility.
Beneath the vast Texan sky, where dust often dances with the ocean breeze, SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica stands abuzz with anticipation. The towering presence of Starship, an ambitious giant that dwarfs even the Statue of Liberty, readies itself for yet another celestial ballet—a dance that might redefine our reach beyond the stars.
This colossal vehicle, at 403 feet tall, is not merely a marvel of engineering but a cornerstone of Elon Musk’s vision to transport humanity to Mars. The next planned orbital test aims to demonstrate the enhanced reliability of its upper-stage spaceship, fortified with upgrades after its previous fiery disintegration over the Caribbean. The debris, scattering over the serene beaches of the Turks and Caicos, underscored the challenges that accompany pioneering innovation.
However, before the colossal rocket can soar into the heavens once more, it contends with the grounding weight of regulations. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has demanded a thorough investigation into the January mishap—a stark reminder that even the most revolutionary dreams tread a precarious path between innovation and oversight. Yet, the FAA, under pressure, has signaled tentative approval for the next launch, albeit with a cloud of scrutiny over SpaceX’s operational audacity.
Meanwhile, the shadow of governmental influence looms large over the proceedings. As Elon Musk, the world’s wealthiest individual, wields his burgeoning power, allegations surface suggesting that his sway might extend beyond engineering prowess to influence regulatory bodies. Reports hinting at veiled threats to the FAA employee job security have sparked an insightful dialogue on the balance of power between innovation-driven companies and the regulators entrusted to uphold public safety and ethical standards.
During this dance between technological advancement and regulatory oversight, NASA watches intently. The space agency’s ambitions to once again caress the lunar surface rest significantly on a modified version of Starship, designated as the future lunar lander for the Artemis program. It signifies a symbiotic yet singular reliance on private enterprise for public frontiers.
For now, the forthcoming mission will once again test the bounds of possibility as SpaceX attempts to deftly catch its descending booster—a feat reminiscent of sci-fi cinematics, achieved previously with precision. Starship will mimic deploying satellites into orbit, though these will gracefully fall back to Earth in a controlled atmospheric burn, a testament to the realm where aspiration meets engineering.
As the engines ignite and the colossus begins its ascent, we’re left to ponder not just on the echoes of its thrusters, but on the broader implications. In a world reaching towards the stars, the delicate dance of power and oversight continues to define our terrestrial boundaries. Starship’s odyssey is not merely about where we can reach, but how we choose to get there—reminding us that progress, though thrilling, demands a thoughtful balance between dreams and accountability.
Exploring the Intricacies of SpaceX’s Starship: A New Chapter in Space Exploration
The Evolution of SpaceX’s Starship
SpaceX’s Starship, a towering 403-foot engineering feat, is integral to Elon Musk’s ambitious vision to colonize Mars. The vehicle’s impressive scale, larger even than the iconic Statue of Liberty, symbolizes humanity’s aspirations to explore the cosmos. With its next orbital test flight, SpaceX aims to showcase enhanced reliability and the improvements made since its previous testing phase. This ongoing development highlights SpaceX’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s technologically feasible.
How-To: Preparing a Space Vehicle for Launch
1. Design Upgrades: Following a test failure, engineers must meticulously analyze data to identify weaknesses. This involves redesigning components to enhance durability, particularly for severe conditions encountered during space travel.
2. Regulatory Approval: Securing approval from bodies like the FAA is crucial. This often means undergoing rigorous review processes to ensure compliance and safety standards are met.
3. Launch Preparations: This phase involves testing all systems, fueling, and conducting final checks to ensure readiness. The objective is to prevent technical malfunctions that could jeopardize the mission.
Real-World Use Cases: SpaceX’s Starship
Starship goes beyond just transporting humans. Its applications include deploying satellites into orbit, carrying research missions, and potentially becoming a linchpin for commercial space travel. As part of NASA’s Artemis program, a modified Starship will serve as a lunar lander, pivotal for future missions to the Moon.
Controversies & Limitations
Elon Musk’s SpaceX finds itself at the intersection of innovation and regulation. Allegations of exerting undue influence over regulatory bodies highlight the complex relationship between private aerospace enterprises and governmental oversight. This raises ethical questions about power dynamics and accountability in the industry.
Market Forecasts & Industry Trends
The commercial space transport market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing interest in space tourism and private space missions. SpaceX is at the forefront of this industry, challenging traditional aerospace companies and prompting advancements that lower costs and increase access to space.
Pros & Cons Overview
Pros:
– Innovative Technology: Advanced engineering design allows for progressively ambitious missions.
– Cost Efficiency: Reusability of the Starship components promises to reduce costs per launch.
– Visionary Goals: Aims to make space travel attainable for civilians and support planetary exploration.
Cons:
– Regulatory Challenges: Navigating government regulations can delay progress.
– Risk Factors: Any failure during testing could stall development and impact reputation.
– Financial Burden: High costs are associated with ongoing research and development.
Actionable Recommendations
– Stay Informed: Following announcements from SpaceX and NASA can provide insights into current capabilities and future missions.
– Engage with Space Communities: Participating in forums and discussions can offer deeper understanding and networking opportunities with industry enthusiasts.
– Educational Opportunities: Pursue learning in fields like aerospace engineering or participate in space exploration events to foster personal growth in the industry.
For more on space exploration and ongoing advancements, visit SpaceX or check out NASA for official updates and missions.
SpaceX’s Starship continues to captivate the world as it aims to define the future of space travel. As it prepares for its next launch, the project not only reflects technical prowess but also emphasizes the need for ethical and calculated advancements in human endeavors.